The dark side of Congo's cobalt rush
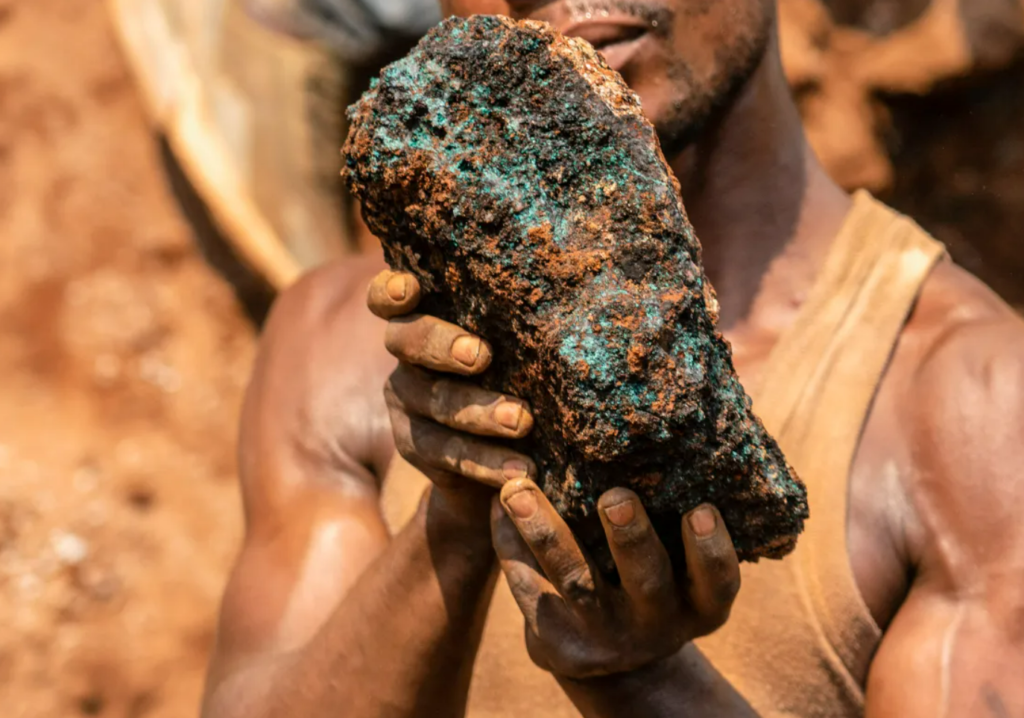

Cobalt is an essential mineral used in the production of batteries. It can be found in every one of your smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Approximately 200,000 miners work on cobalt mines in Congo, and another one million workers earn their livelihood from activities related to cobalt. Of these 200,000 miners, 40,000 are reported to be children, some as young as six years old.
DR Congo is the world’s largest producer of cobalt from mines, accounting for more than 70% of worldwide cobalt mine production in 2021.
The mining sector makes up 32% of Congo’s GDP.
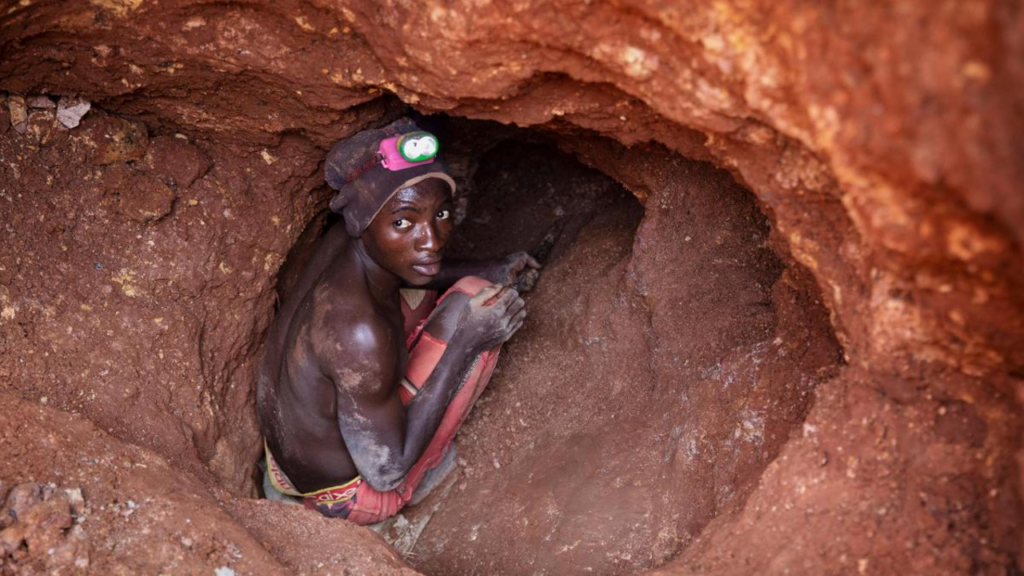
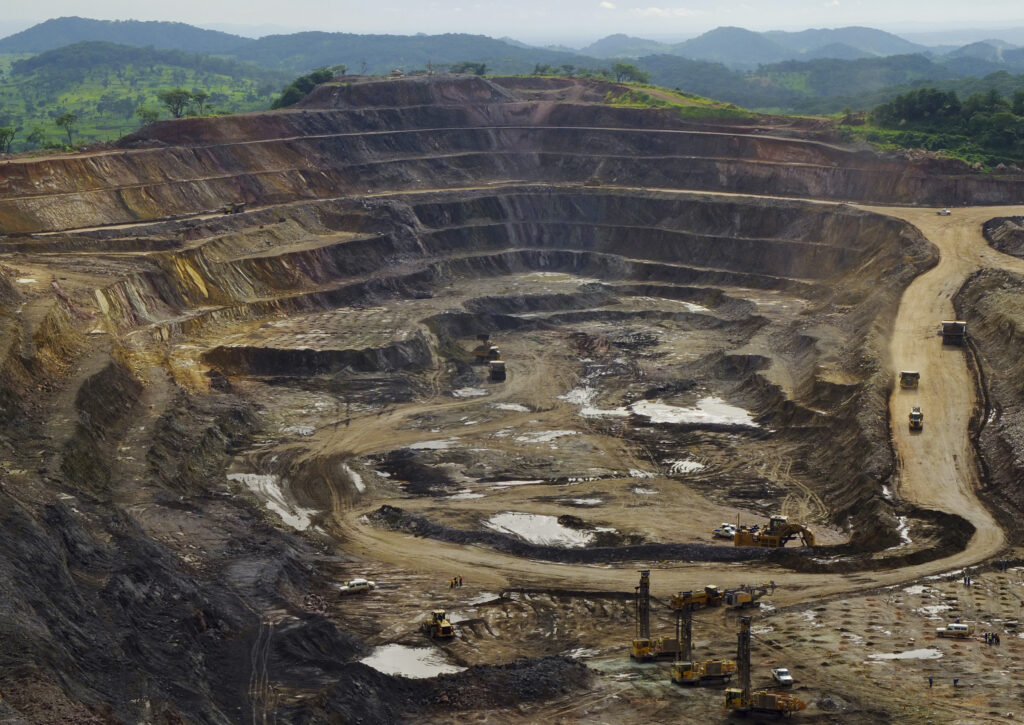


Although cobalt is an important resource in Congo, there are concerns that the Congolese people are not enjoying the full benefits of its production.
The largest cobalt mine in Congo is owned by Chinese mining multinational, China Moly. The next three largest are all owned by the Swiss company, Glencore.
The average wage for Congolese miners is between $2 to $3 per day, which is higher than the national minimum wage of $1.20.
However, most of the profits generated by the foreign multinationals go to foreign shareholders. They have also been criticized for tax evasion and bribery.
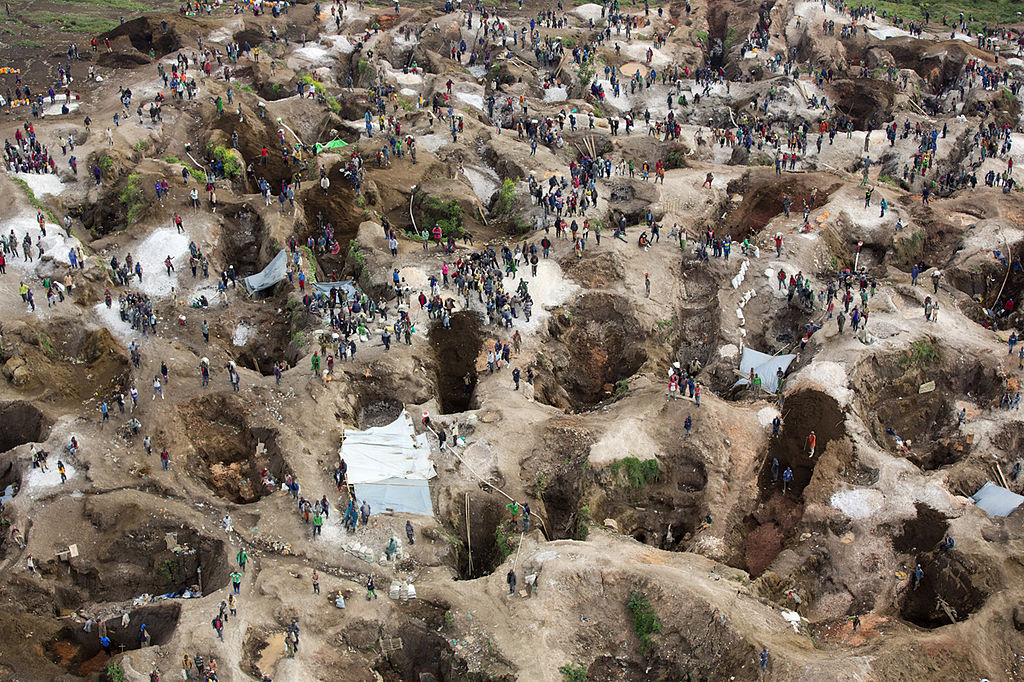

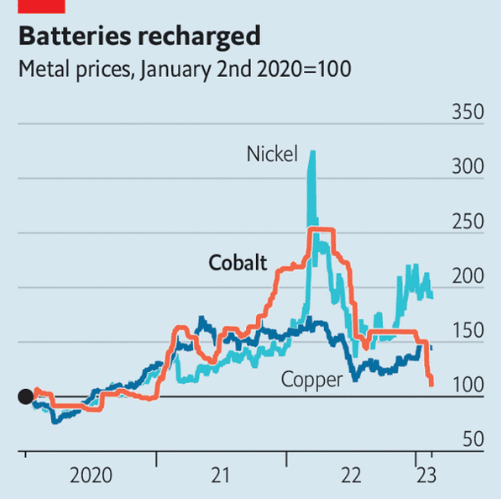
Since the end of Covid-19 lockdowns, demand for electronics has fallen significantly because people are spending more time outdoors.
At the same time, Indonesian exports of cobalt have risen to 18,000 tonnes this year, up from virtually none just a few years ago.
These market changes have caused the price of cobalt to fall from $82,000 a tonne to $35,000 today.
Questions
- Explain a typical trade pattern of a developing country such as Congo. (3)
- Draw a supply and demand diagram for cobalt showing the impact of the changes described in the final paragraph. (3)
- Analyse the disadvantages of Congo’s commodity dependence. (6)
- Evaluate to what extent Congo has benefitted from globalisation. (12)
Question 3:
- How dependent is Congo on cobalt?
- Would impact would the change in price of cobalt have?
Question 4:
- What are the benefits?
- What are the drawbacks?
- What does it depend on?
